Problem
Given two binary search trees root1 and root2.
Return a list containing all the integers from both trees sorted in ascending order.
Example 1:
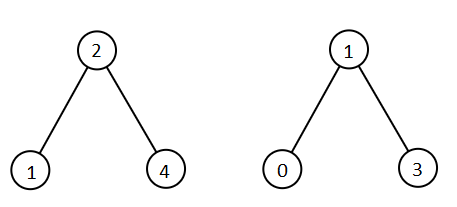
1
2
| Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3]
Output: [0,1,1,2,3,4]
|
Example 2:
1
2
| Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
Output: [-10,0,0,1,2,5,7,10]
|
Example 3:
1
2
| Input: root1 = [], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
Output: [0,1,2,5,7]
|
Example 4:
1
2
| Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = []
Output: [-10,0,10]
|
Example 5:
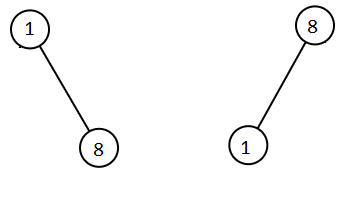
1
2
| Input: root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1]
Output: [1,1,8,8]
|
Constraints:
- Each tree has at most
5000 nodes.
- Each node’s value is between
[-10^5, 10^5].
Analysis
这道题是二叉树和数组的结合。第一种最简单的方法就是直接遍历二叉树获得里面的所有元素,然后对数组进行排序就可以了。这样做已经是比较高效率了,但是问题是我们没有利用到二叉树的信息。
题目给出的信息是两个搜索二叉树,我们知道对搜索二叉树进行中序遍历是能够得到有序的数组的。所以思路就转换为我们先对两颗BST进行中序遍历后,得到两个各自有序的数组,然后再合并这两个有序的数组,合并两个有序的数组就非常简单了。
Solution
无
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAllElements(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
vector<int> result1;
vector<int> result2;
traverse(root1, result1);
traverse(root2, result2);
int i = 0, j = 0;
int size1 = result1.size();
int size2 = result2.size();
vector<int> result;
while (size1 + size2 != result.size()) {
if (i == size1) {
result.push_back(result2[j++]);
} else if (j == size2) {
result.push_back(result1[i++]);
} else {
result.push_back((result1[i] > result2[j])? result2[j++]: result1[i++]);
}
}
return result;
}
private:
void traverse(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& result) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
traverse(root->left, result);
result.push_back(root->val);
traverse(root->right, result);
}
};
|
Summary
这道题目的关键就在于利用BST的性质去中序遍历得到两个有序的数组,再进行合并。这道题的分析到这里,谢谢!



