Problem
Given a binary tree, each node has value 0 or 1. Each root-to-leaf path represents a binary number starting with the most significant bit. For example, if the path is 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1, then this could represent 01101 in binary, which is 13.
For all leaves in the tree, consider the numbers represented by the path from the root to that leaf.
Return the sum of these numbers.
Example 1:
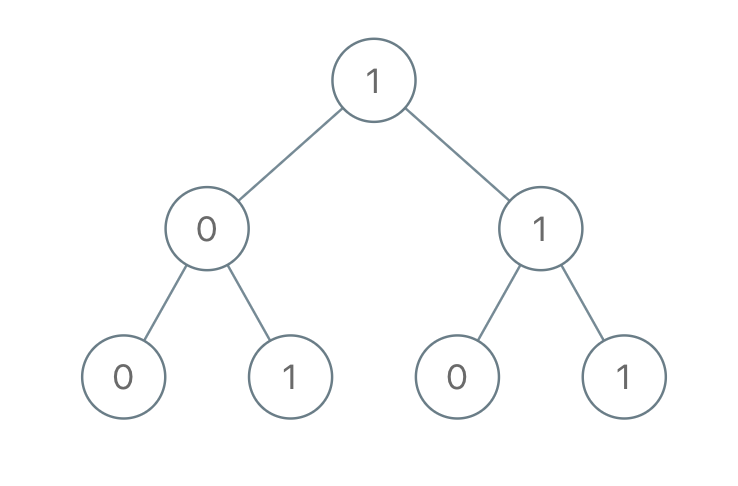
1 | Input: [1,0,1,0,1,0,1] |
Note:
- The number of nodes in the tree is between
1and1000. - node.val is
0or1. - The answer will not exceed
2^31 - 1.
Analysis
二叉树深度遍历的变种题目。每一条从root到leaf的节点的路径都代表着一个二进制数,题目要求我们求出所有二进制数的和。有两种做法,第一种是做深度遍历,计算出所有从root到leaf的路径,然后一个一个计算。这种方法是比较繁琐的,没有很好地运用到数字运算的本质。第二种则是巧用了进制数的运算,一位一位加上去,所以反映到二叉树就是一个节点一个节点添加,本质上还是做一个遍历,对于二叉树来说,使用递归的方式是最简单的。
因为root是最高位,所以递归下去的话就是父节点乘2再加上本节点的值。每次递归我们只需要根据父节点传下来的值,加上自己的值,然后递归去左右子树的时候带上这个值就可以了。
Solution
无
Code
1 | /** |
Summary
这道题的本质就是用一个递归去遍历,在遍历的过程中计算出到本节点的和,然后进一步传递给子树(传给左右子树都是相同的)。这道题的分析到这里,谢谢!

