Problem
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Follow up: A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward. Could you devise a constant space solution?
Example 1:
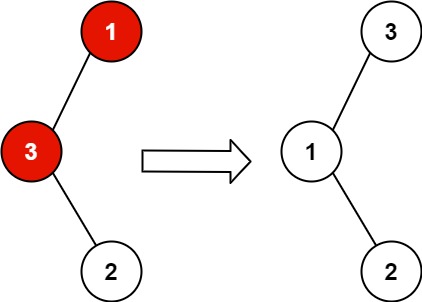
1 | Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2] |
Example 2:
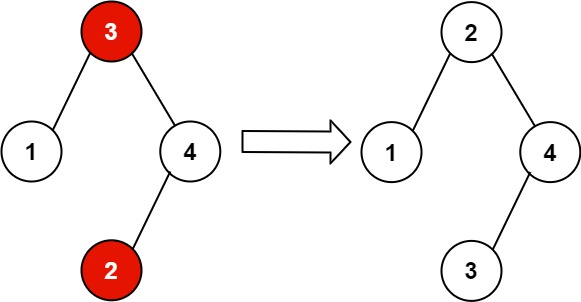
1 | Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
Analysis
这道题目是二叉树比较新颖的题目,题目给定的BST中,有两个节点的位置错乱了,不满足BST的要求,要求我们恢复这个BST的正确顺序。
BST的正确顺序实际上就是一个有序性,比较简单的做法是直接对BST进行中序遍历,得到数组之后,肯定有两个位置的顺序是乱的。然后对这个数组排序,再把结果放回到BST中。这个做法不单止是对两个位置错乱的情况有效,对任意数量位置错乱的BST都是有效的。
但是题目有一个Follow up是要求用$O(1)$的空间复杂度完成,上面说的方法用了额外的空间,所以还有优化的空间。最优的解法应该是用Morris遍历,这是一种空间复杂度为常数级别的二叉树遍历方法。在这里我也顺便分享一下我的理解。
首先看看以往我们使用的遍历方法,大多都是通过递归或者是循环+栈/队列进行的。相信无论是递归还是循环的方法,大家coding都没有问题,但是有没有想过为什么要这样做呢?很根本的一个原因是:当我们遍历到叶子节点的时候,需要返回到父节点,所以就需要有额外的空间去存放,这样才能返回去。Morris遍历既然是$O(1)$空间复杂度的,自然也是要从这个问题入手。它是怎么解决的呢?以中序遍历为例,当遍历完左子树之后,就需要回到root,这个时候,morris遍历直接把左子树的最右子节点指向root,所以当遍历完成后,就能够通过这个子节点回到root。因为不能破坏树的结构,所以第一次在root的时候,先找到这个左子树的最右子节点,指向root,这样能够保证遍历完root的左子树后,能够返回到root;第二次真正遍历到的这个节点的时候,再把它的指针重新置空。
Solution
普通的做法要用额外的空间存放中序遍历的结果,因为需要对值进行排序,所以用两个数组分开存放,一个是存Node指针,一个是存值。只需要对值进行排序,按顺序放回到Node指针中即可。
这里简单分享一下Morris遍历的步骤(当前节点为current):
- 如果
current没有左子树,current向右子树移动(current = current->right); - 如果
current有左子树,找到左子树上最右子节点,这个节点记为mostRight:- 如果
mostRight的右指针为空,让其指向current,current向左子树移动(current = current->left),这相当于第一次先找到这个节点,记录下返回的信息; - 如果
mostRight的右指针指向current,让其指向空,current向右移动(current = current->right)
- 如果
Code
1 | /** |
Morris遍历
1 | /** |
Summary
当前只分享了这道题目最简单的做法,最优的做法还在学习中。从简单的这个做法中也能得到一些启示,有些时候为了做题的方便,当没有过多限制的时候,可以用额外的空间去简化自己的算法。同时我们也了解了一种新的神级二叉树遍历方法——Morris遍历。这道题目的分享到这里,谢谢!

