Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
Return the smallest subtree such that it contains all the deepest nodes in the original tree.
A node is called the deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is tree consisting of that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Note: This question is the same as 1123: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
Example 1:
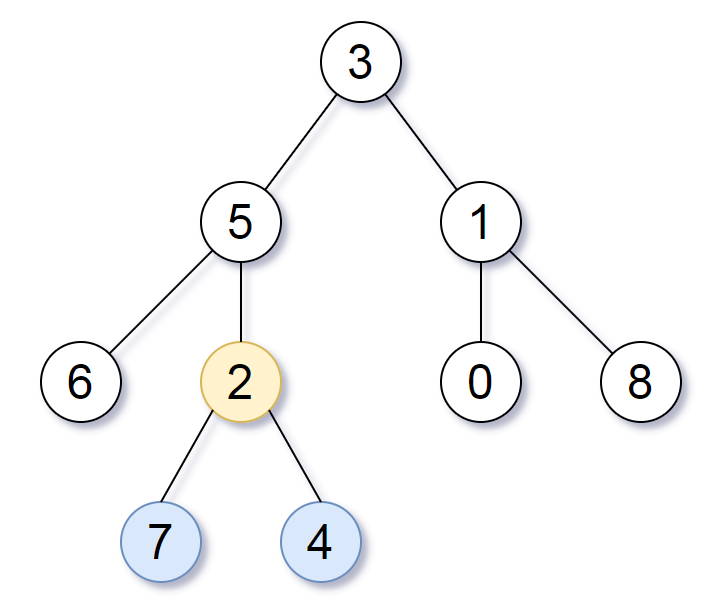
1 | Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [1] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
Analysis
这是一道二叉树高度相关的题目,要求找到包含最深节点的最小子树。遇到这类题目很自然地就会往递归方面考虑。利用递归计算树的高度并不难,这道题目难的地方在于如何找到最深的那棵树,是否需要把节点记录下来?
我们先从题目给的example入手分析一下,可以看到对于以2为根的这颗树来说,2的左子树和右子树的深度都是1。往2的父节点看,以5为根的这棵树来说,它的左子树深度(2)比右子树(3)要小,所以选择的是它右子树。实际上题目给出的这个例子非常好,它把两种情况都覆盖了。对于某个 根节点root来说:
- 如果它的左、右子树高度相等:那么它就是要返回的节点,因为两个子树包含的节点的深度都是一样的;
- 如果它的左、右子树高度不相等,那么它就不可能是最小的子树的根节点。所有就要往深度更大的那个子树去寻找。
Solution
写一个递归的函数去计算深度,再写一个递归去计算比较每个节点的左右子树,相当于是两个递归依次进行。
Code
1 | /** |
Summary
这道题目虽然看上去要求有点复杂,但是本质还是二叉树深度相关的内容,利用递归能够很方便解决。这道题目的分享到这里,谢谢您的支持!

