Problem
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) that therandompointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
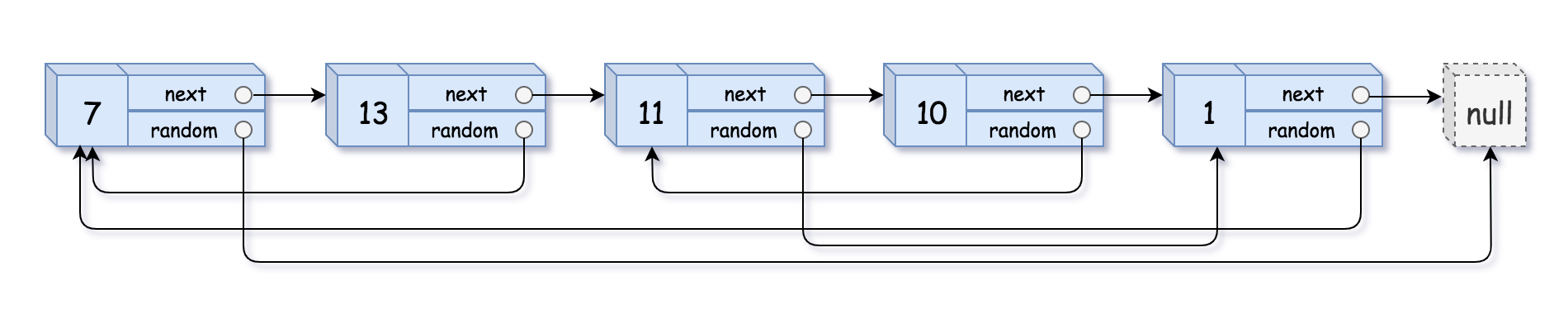
1 | Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] |
Example 2:
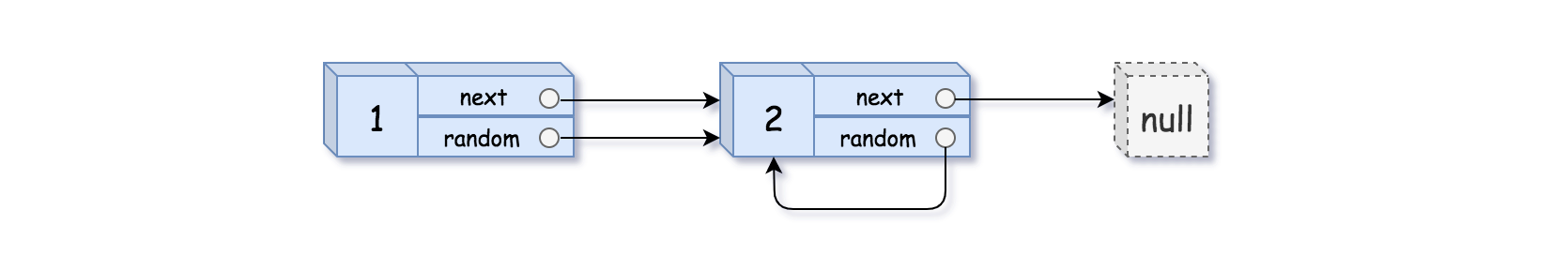
1 | Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]] |
Example 3:
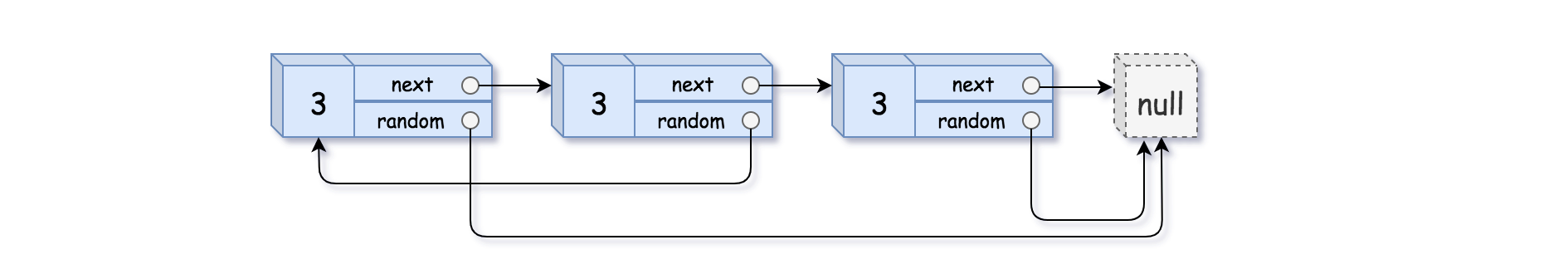
1 | Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] |
Example 4:
1 | Input: head = [] |
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomisnullor is pointing to some node in the linked list.
Analysis
题目要求我们deep copy一个链表,这个链表比较特殊,除了next指针外,还有一个random指针,指向链表中的任意一个元素(或者是NULL)。虽然链表的结构是复杂了,但是理清思路后,这个深拷贝和普通链表没什么不同。
首先我们不考虑复制random部分,只copynext指向的节点,这个是非常简单的。之后我们再对每一个节点复制他的random指针,这是因为第一次遍历完后,能够保证所有节点都被复制了。因为第二遍复制random的时候需要在新旧链表之间建立对应关系,所以这里用到了map。在第一遍遍历的时候就建立好新旧链表直接每个节点的关联关系。
Solution
无
Code
1 | /* |
Summary
这是一道链表深拷贝的进阶题,虽然增加了一个random指针使得链表的结构变得负责,但复制的原理还是一样的。这里也借助了map对random部分进行拷贝。这道题目的分享到这里,谢谢您的支持!

