Problem
You are given an m x n integer matrix heights representing the height of each unit cell in a continent. The Pacific ocean touches the continent’s left and top edges, and the Atlantic ocean touches the continent’s right and bottom edges.
Water can only flow in four directions: up, down, left, and right. Water flows from a cell to an adjacent one with an equal or lower height.
Return a list of grid coordinates where water can flow to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 1:
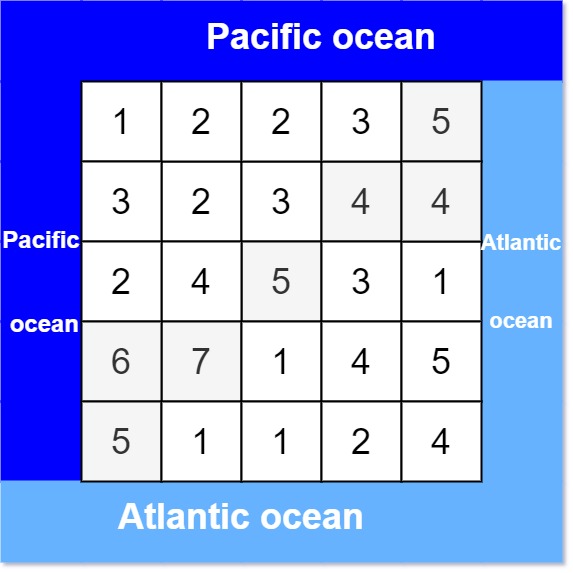
1 | Input: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]] |
Constraints:
m == heights.lengthn == heights[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2001 <= heights[i][j] <= 105
Analysis
题目的本质是一个二维矩阵遍历的问题,题目的意思有点复杂。首先题目说左边和上边是太平洋,右边和下边是大西洋,每个位置上的数值是高度,遵循水往低处流的原则,问有哪些位置的水可以最终流入海洋。其实这个就是一个连通性问题,在矩阵中任意选一个点,连通的条件是当前位置的值比下一步位置的值要大(或等于),最后看看是否两个海洋都能到达即可。
这里涉及到一个复杂性的问题,原因是,如果要对矩阵中所有的位置都检查一遍,计算复杂度很高,而且会有很多重复计算的情况。我们不妨逆向思维,从四条边出发,反向寻找。从左边和上边出发,找到矩阵中能连通的点;同理,从右边和下边出发,也找到矩阵中能够连通的点,然后把这两个集合的点求一个交集即可。
Solution
需要注意,在反向处理时,连通的条件就变为当前位置的值必须要严格小于下一个位置的值。
Code
1 | class Solution { |
Summary
这是一道比较简单的二维矩阵连通问题,其实原理还是DFS,只是需要变换一下遍历的方向。这道题目的分享到这里,感谢你的支持!

