Problem
Given the head of a singly linked list, return true if it is a palindrome.
Example 1:
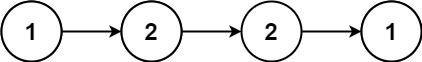
1 | Input: head = [1,2,2,1] |
Example 2:
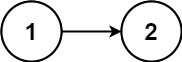
1 | Input: head = [1,2] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9
Follow up: Could you do it in time and space?
Analysis
题目给出一个链表,要求判断是否回文链表。判断回文如果是放在数组中做,就很简单了,因为我们可以通过下标直接访问,所以用头尾指针不断对比即可。但是放到链表中,就不能这么做了。对于链表,我们只能一个方向遍历,但是判断回文显然要从两个方向遍历,为了实现两个方向遍历,在不使用额外空间的情况下,只能把链表翻转。
有了翻转这个思路,题目就变得简单了,我们只需要从中间把链表翻转,然后对两部分逐一比较就能判断是否回文了。
Solution
这里我们只需要对链表的一半进行翻转,显然是对后半部分翻转比较容易(不需要考虑很多边界条件)。这里不需要对奇偶数量的节点做特殊处理,因为在对比前后两部分的时候,我们只需要对比两条链表上都有的节点。
Code
1 | /** |
Summary
这道题目虽然是判断回文数,但其本质考察的是部分翻转链表,因此翻转链表这个知识点是非常关键的,包括全部翻转、部分翻转。这道题目的分享到这里,感谢你的支持!

