Problem
Implement the BSTIterator class that represents an iterator over the in-order traversal of a binary search tree (BST):
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)Initializes an object of theBSTIteratorclass. Therootof the BST is given as part of the constructor. The pointer should be initialized to a non-existent number smaller than any element in the BST.boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there exists a number in the traversal to the right of the pointer, otherwise returnsfalse.int next()Moves the pointer to the right, then returns the number at the pointer.
Notice that by initializing the pointer to a non-existent smallest number, the first call to next() will return the smallest element in the BST.
You may assume that next() calls will always be valid. That is, there will be at least a next number in the in-order traversal when next() is called.
Example 1:
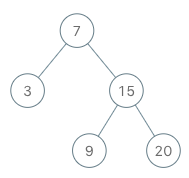
1 | Input |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 106- At most
105calls will be made tohasNext, andnext.
Follow up:
- Could you implement
next()andhasNext()to run in averageO(1)time and useO(h)memory, wherehis the height of the tree?
Analysis
接下来三篇博客我将介绍Iterator实现的题目,之前也提到过这类问题的解法大致有两种:
- 在构造函数直接打平成数组,然后用一个下标去控制访问,优点是实现起来相对简单,缺点是针对无限长度的数据结构无法实现,而且面试一般不给用这种;
- 按需计算,也就是维护当前的状态,只有当调用到了
next()的方法我们才往后走,一般配合queue、stack等数据结构使用,这是通常的解法,后面的题目我都会focus在这种解法上。
回到这道题目,是需要实现一个BST的Iterator,遍历的顺序是中序遍历,二叉树中序遍历非迭代的实现就是使用stack,本质上和这道题目一模一样。我们先把所有的左节点都放到stack中,每次调用next()时取出栈顶元素,栈顶元素就是我们需要返回的结果,然后往右走一步node = node->right,再把所有的左子树放到stack中,当然也包括node本身。至于hasNext()直接通过stack是否为空判断即可。
Solution
无。
Code
1 | /** |
Summary
这道题目是一个非常简单的BST的iterator实现,和BST中序遍历非迭代实现本质上是一样的。这道题目的分享到这里,感谢你的支持!

