Problem
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree.
Given a tree of n nodes labelled from 0 to n - 1, and an array of n - 1 edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between the two nodes ai and bi in the tree, you can choose any node of the tree as the root. When you select a node x as the root, the result tree has height h. Among all possible rooted trees, those with minimum height (i.e. min(h)) are called minimum height trees (MHTs).
Return a list of all MHTs’ root labels. You can return the answer in any order.
The height of a rooted tree is the number of edges on the longest downward path between the root and a leaf.
Example 1:
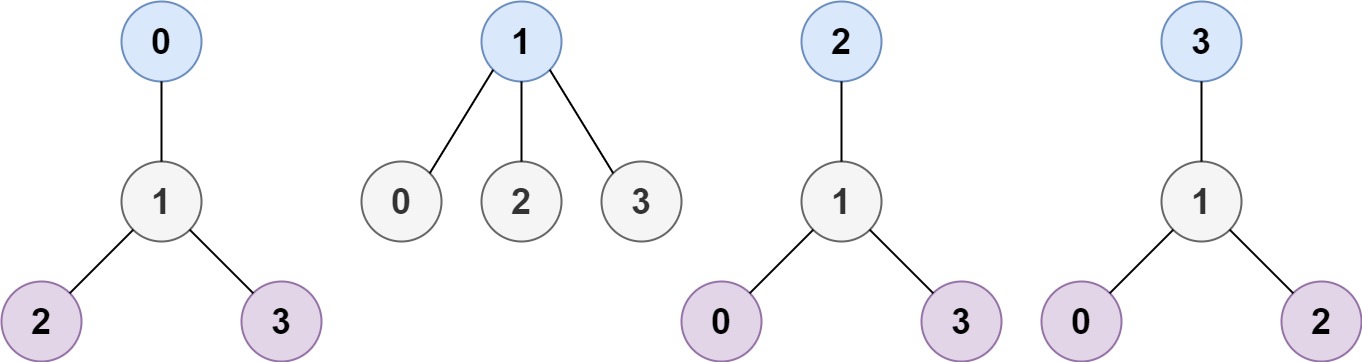
1 | Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,0],[1,2],[1,3]] |
Example 2:
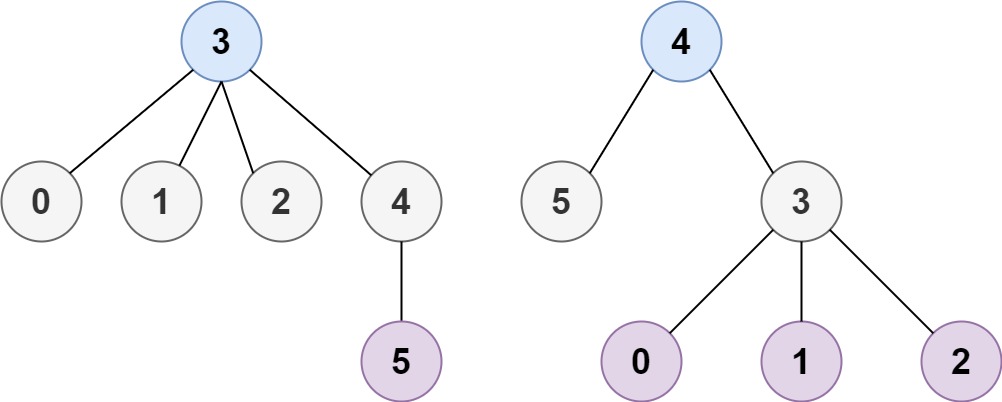
1 | Input: n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: n = 1, edges = [] |
Example 4:
1 | Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1]] |
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 104edges.length == n - 10 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- All the pairs
(ai, bi)are distinct. - The given input is guaranteed to be a tree and there will be no repeated edges.
Analysis
题目是以树为背景描述的,给出一个图,要求我们找到让这棵树的高度最小的root。虽然这个看上去是和树有关系,但实际上这个就是单纯的图问题。要求树的高度最少,我们先来看看怎么样才能做到?
其实这个是一个很简单的问题,比如有一条绳子,怎么拿起来才能让他的长度最短,当然是从中间拿起来。这个问题也是一样的,如果用叶子节点作为root的话,那么从一个叶子节点到另一个叶子节点,就需要走比较长的路径。所以做法就是逐层剔除掉叶子节点,最后留下来的就是root。
逐层剔除实际上和层次遍历有点类似,首先根据给出的信息构建邻接矩阵,然后用一个queue做层次操作。对于每一层,剔除掉叶子节点,剔除后如果发现新的叶子节点,则push到queue中,等待下一层的处理。最后剩下的1-2个节点就是root了。注意是1或2,但是不可能是3,因为有三个的话,必定可以删除掉两个子节点。
Solution
对于某个节点来说,我们只关心它是否和另一个节点相连,这道题目只考虑存在关系,所以用set存某个节点相连的节点即可。
逐层剔除叶子节点和层次遍历非常像,相信不会太难。注意判断叶子节点的方法是查看邻接矩阵的set是否为1。然后复用n这个变量,表明当前图还有多少个节点,如果是小于等于2则说明剔除完成,剩下的就是结果。
Code
1 | class Solution { |
Summary
一直以来图方面的题目做得比较少,之前做过的也是一些遍历相关的。这道题目在遍历的基础上增加了一些逻辑,在coding的时候这类题目一定要能够快速构建邻接矩阵,根据需要选择set或者vector。同时这道题目虽然是以树的背景描述,但实质的问题还是图,要找到这个突破点并不容易,所以我认为这道题目是非常有必要总结的。这道题目的分享到这里,谢谢!

