Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest consecutive path in the tree.
A consecutive path is a path where the values of the consecutive nodes in the path differ by one. This path can be either increasing or decreasing.
- For example,
[1,2,3,4]and[4,3,2,1]are both considered valid, but the path[1,2,4,3]is not valid.
On the other hand, the path can be in the child-Parent-child order, where not necessarily be parent-child order.
Example 1:
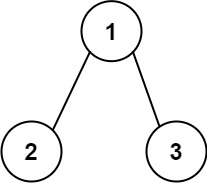
1 | Input: root = [1,2,3] |
Example 2:
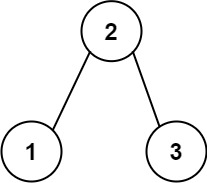
1 | Input: root = [2,1,3] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -3 * 104 <= Node.val <= 3 * 104
Analysis
这是一道二叉树的题目,题目要求找出树中最长的连续路径,可以是递增的,也可以是递减。这里的路径指的是任意两个节点。先说一种很直接的方法,把树变成一副图,用一个map存储每个节点的父节点,然后做一遍BFS/DFS,找到最长的连续路径。但似乎这样就没有充分利用到了二叉树的特点,二叉树题目一般来说都可以通过递归来解决,那么这里我们能不能也用递归呢?
答案当然是可以的。那我们需要在节点直接传递什么信息呢?对于父节点来说,如果它的左子树+它本身+它的右子树构成了一条连续的路径,那么长度应该是左子树路径的长度+右子树路径的长度+1。而我们这里又分递增和递减,因此每个节点应该返回两个值,一个是递增的路径长度,另一个是递减的路径长度。
然后在处理节点时,比较root->val和root->left->val(如果存在),以及root->val和root->right->val(如果存在),去判断是否构成连续的路径,然后把对应的长度相加起来。需要注意,经过节点本身的最长路径应该是递增+递减,因为节点本身是一个中间点,然后维护一个最大值。
Solution
无。
Code
1 | /** |
Summary
这道题目是二叉树中有关路径长度的题目,一般来说这类题目都是能使用递归求解,而递归函数的返回值会包含多个信息,在这里就是包含了递增和递减的路径长度。这道题目的分享到这里,感谢你的支持!

